What is Pre Implantation Genetic Testing (PGT)?
Previously used terms like PGD (Pre Implantation Genetic Diagnosis) and PGS (Pre Implantation Genetic Screening) has been replaced by a more appropriate term called PGT (Pre Implantation Genetic TESTing). PGT is defined as a test that is performed on few cells that are extracted (embryo biopsy) from the Embryo (mostly Day 5 Blastocyst) for ruling out genetic abnormalities.
please read the following blogs to understand basics of genetic abnormalities & testing
How is PGT done?
PGT is done in conjunction with IVF Cycle, wherein the embryo’s formed during the cycle, are biopsied to extract a few cells and those cells are sent to a genetic lab for testing their genetic competency.
The following diagram illustrates the entire process followed during an IVF – PGT Cycle:
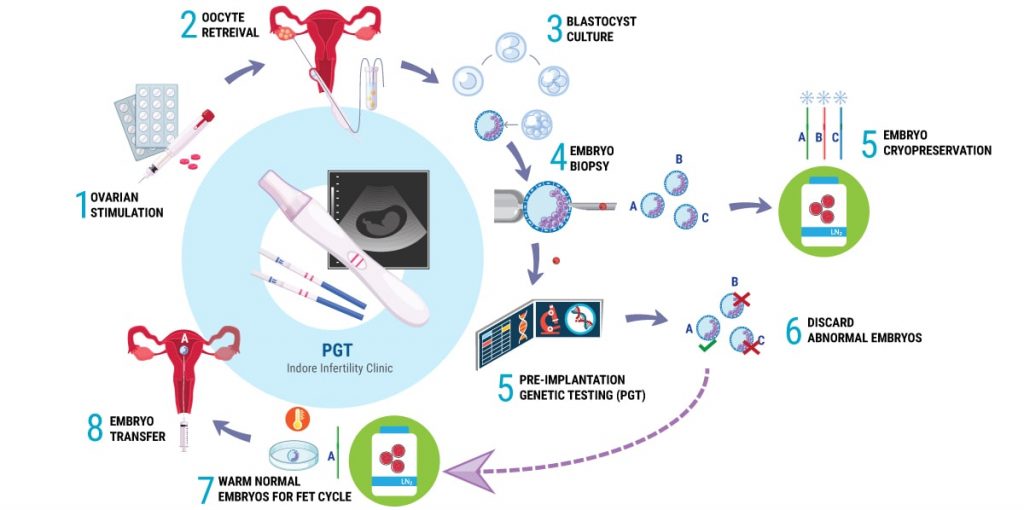
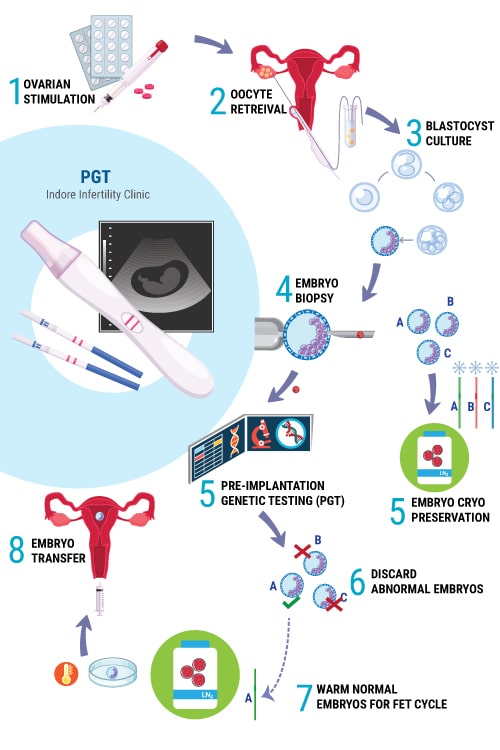
As shown in the illustration, up until Step 4 of Embryo Biopsy, the events in the IVF Cycle are similar to a regular IVF Cycle i.e
Step 1 : Ovarian Stimulation (with Follicular Monitoring)
Step 2: Oocyte Retreival or Ovum Pick-Up (And later Fertilization in the IVF lab)
Step 3: Embryo Culture (Upto Blastocyst Stage – Day 5 to 6 Embryo)
Step 4 : Embryo Biopsy (Extracting few cells from Embryo)
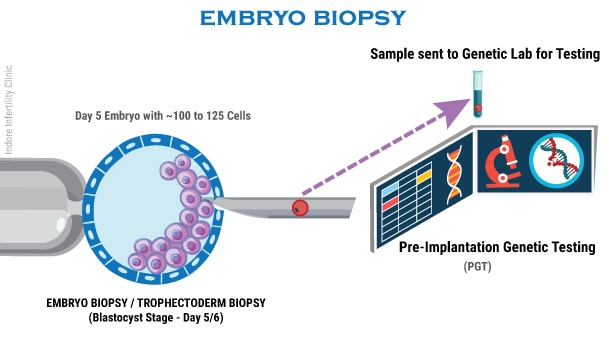
Embryo Biopsy is usually performed on Day 5 or Day 6 when we have fully expanded Blastocyst. During Embryo Biopsy, a few cells (about 7 to 10 cells) are extracted from the Blastocyst using Biopsy needle and the extracted cells are then safely transported to a Genetic Lab for testing.
Step 5 (Genetic Lab): Pre-Implantation Genetic Testing
The extracted cells are tested using novel NGS – Next Generation Sequencing technique which is a kind of molecular genetic testing which analyses all 23 pairs of chromosomes in details.
PGT report usually takes about 1 to 3 weeks depending upon the type of testing requested (PGT-A, PGT-SR or PGT-M). Results of PGT indicate which embryo is normal and which ones are abnormal.
Step 5 (IVF Lab): Embryo Cryopreservation
Meanwhile in the IVF Lab, the Blastocysts that underwent biopsy on Day 5/6 are then tagged and cryopreserved for later use.
Step 6 (Arrival of PGT Result): Results indicate genetic competency of Embryo’s. The ones that have multiple abnormalities are discarded.
Step 7 and Step 8: FET Cycle
Patients are then prepared for Frozen Embryo Transfer Cycle by giving medication to prepare the endometrium. Based on the report of PGT, a normal embryo with potential to implant is transferred to the patient.
How much time does it take to get PGT Results?
Embryo Biopsy result from a genetic lab usually takes one to three weeks depending on the type of test requested.
PGT-A and PGT-SR usually takes about 7 to 10 days.
PGT-M takes about a maximum of 3 weeks. During PGT-M patients can also be requested to get their blood Karyotyping test done before the Embryo biopsy.
Is embro biopsy a safe procedure?
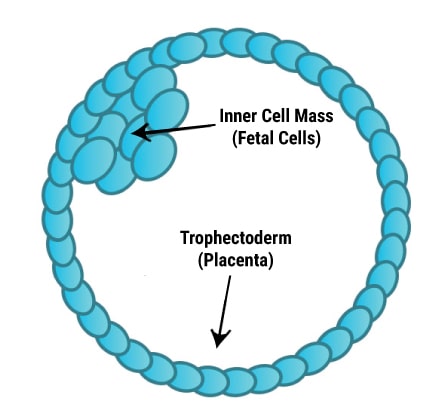
A human blastocyst (Day 5 Embryo) has 2 types of cells:
Trophectoderm: Cells that forms the placenta
ICM (Inner Cell Mass) – Cells that form the fetus
Since Blastocysts consists of more than 100 cells, it is possible to extract 7 to 10 cells from the Trophectoderm without affecting the implantation potential of the embryo much. Analyzing more cells in the genetic lab brings better accuracy in the test results.
In Blastocyst stage Biopsy, a few cells are extracted from the outermost layer of the Blastocyst (Trophectoderm). This approach is considered to be the safest approach for biopsy without impacting the implantation potential of the embryo to a great extent.
What is the cost of PGS or PGT - Pre Implantation Genetic Testing or Pre Implantation Genetic Screening of Embryos?
The cost of Pre Implantation Genetic Screening or Testing (PGT or PGS) involves charges of performing Embryo Biopsy as well as charges of genetic testing performed on embryo.
Since the charge for PGS have a fixed as well as variable component based on number of Blastocysts formed, it is best to discuss the charge after getting your case reviewed by the doctor.
These charges are charged over and above the charge of a normal IVF/ ICSI Blastocyst Transfer Cycle.
Video demonstration of Embryo Biopsy Process performed on Fully Expanded Grade 4AA Blastocyst.
What is the accuracy of PGT?
PGT of embryo’s started in 1990’s and has evolved not only in the biopsy technique, but also in achieving higher accuracy in reporting by using novel molecular testing techniques like Single Nucleotide Polymorphism microarrays (SNP Arrays), Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR) and Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS).
The first technique used (1992) for PGT was Fluorescence in Situ Hybridization (FISH). FISH was subsequently adopted all over the world for the analysis of numerical errors in chromosomes and some structural abnormalities of few selected chromosomes i.e. FISH analysis was done on predefined chromosomes like Chromosome 13, 18, 21, 22 and sex chromosomes.
With advancement in genetic testing, labs have shifted to using more advanced techniques like NGS (Next Generation Sequencing) that are capable of analyzing the whole genome (all 23 pairs of chromosomes) with greater accuracy.
Before we try and understand the accuracy of PGT, we need to understand the concept of ‘MOSAICISM’
Theoretically all cells of an embryo should have the same number of chromosomes, however in about 10 to 20% of cases embryos contain a mix of both normal and abnormal cells. Such embryo’s are called mosaics and the condition is called mosaicism.
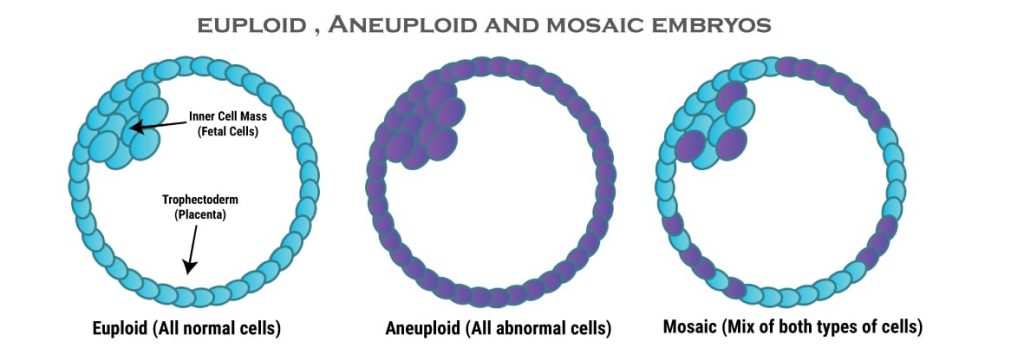
Often times a mosaic embryo undergoes a process called Embryo Self-Correction to correct the abnormal cells, hence there is always a chance that if an embryo has been detected with a few abnormal cells, it may undergo self-correction and result in a healthy live-birth.
PGT-A done on 5 to 10 cells from the Trophectoderm of the Blastocyst, usually reports mosaicism as follows:
If less than 20% Cells are found to be Abnormal (Aneuploid) – Embryo is labelled as Normal (Euploid)
Such Embryos are transferred First.
If 20 to 40% Cells are found to be Abnormal (Aneuploid) – Embryo is labelled as Low level Mosaic.
Such embryo’s are considered for Embryo transfer ONLY if no other normal Embryo’s are available.
If greater than 40% cells are found to be abnormal – Embryo is labelled as Aneuploid (high level mosaics).
Such embryo’s are normally discarded.
We need to consider the following factors while analysing the accuracy and efficacy of PGT:
Rate of False Positive– i.e How many times will the embryo have all abnormal cells that may go undetected in PGT-A ?
PGT-A using NGS is shown to have a very low rate of False Positives of less than 1%.
Rate of False Negatives – i.e How many times will the embryo have normal (Euploid cells) that may be reported as abnormal in PGT and as a result there is a chance of potentially discarding normal healthy embryo’s?
NGS has a very low False Negative rate of less than 0.5%
What are the disadvantages of PGT?
Many factors needs to be considered:
True Representation
Studies suggest that in about 4% cases, the chromosomal makeup of Trophectoderm cells do not match the Inner cell mass cells. Also the 7 to 10 cells that have been biopsied, are randomly picked and there is no study to prove if the abnormal cells are localized or spread out evenly in the Trophectoderm. This adds to the dilemma of performing such an invasive and costly procedure and not being 100% sure of the results.
Misdiagnosis
High frequency of embryo mosaicism and false Positives often lead to discarding embryo’s that would have otherwise resulted in a live healthy pregnancy. This is the most limiting factor ethically.
Invasive
Embryo Biopsy no matter how gentle, is a very invasive procedure and may result in embryonic damage. It needs a highly trained technician with fair amount of practice of biopsy technique.
Till date we have insufficient studies that will clarify the impact of the biopsy procedure on the implantation potential of embryo. Most clinics that do embryo biopsy on regular basis do claim that about 93% of embryos survive the procedure.
Cost of PGT
The most significant disadvantage of PGT is it’s cost. It is still a very costly procedure and definitely not affordable by most. PGT cost can be broken down into two components:
Cost of Biopsy Procedure: Embryo Biopsy involves very expensive instrument that needs a substantial amount of initial investment. These instruments can also be rented on case to case basis, but the rent is pretty high. The cost of trained technician who have prior experience on embryo biopsy adds on to this cost.
Cost of genetic testing of Biopsied cells: Genetic labs charge per embryo. More the numbers of embryo’s that needs to be tested, more the cost.
Final Words
PGT is definitely not for ALL and should NOT be used as a general screening tool for euploidy of embryo’s using PGT-A.
The high rate of embryo mosaicism, false positives and some loss of implantation potential of embryo’s post biopsy technique itself, warrants a very limited use of PGT from case to case basis as of today.
PGT-M or PGT for single gene inherited disorders indeed promises a chance for couples to choose embryo’s that shall not pass on the disorder to future generations. This is a huge relief for patients who may never want their own children to have a limited quality of life. Hence PGT-M in such cases does seem like a logical option.
Genetic Counseling
Consult us If you or or close family member is suffering from a known genetic disorder Thalassaemia (Beta or Alpha) ,Sickle cell Anemia, Haemophilia etc) and you wish to know how it impacts your ability to give birth to a healthy child.
WHATSAPP FOR GENETIC COUNSELING
You might want to read